1. Introduction
For real device like Intel nics, PMD driver creates TX descriptor ring and RX decriptor ring, and then hardware writes to and reads from system memory through DMA.
For emulated device like vhost, there’s no hardware to perform DMA operation. Instead, a UNIX domain socket based mechanism allows to set up the resources used by a number of Vrings shared between two userspace processes, which will be placed in shared memory.
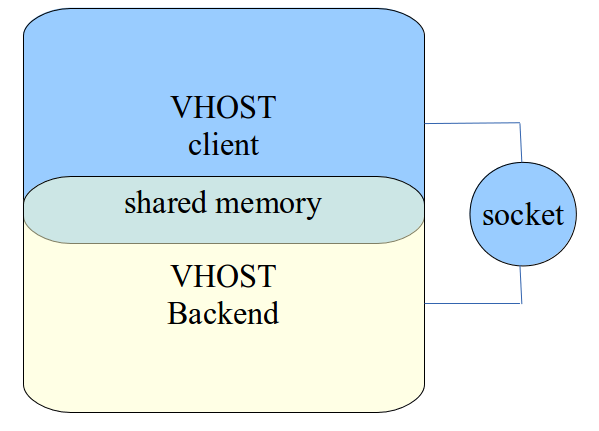
Therefore, DPDK vhost library has to transfer data between shared memory and DPDK mbuf. For this reason, vhost-user dequeue zero copy is introduced to improve the performance from DPDK 16.11 release. Please note that this feature is only used for traffic from vhost-user (dequeue).
And I will investigate the detailed implementation in the next section.
2. Implementation Code
At first, there’s a flag for vhost-user dequeue zero copy.
#define RTE_VHOST_USER_DEQUEUE_ZERO_COPY (1ULL << 2)
And we should enable this flag while registering vhost driver.
int rte_vhost_driver_register(const char *path, uint64_t flags);
Let’s take a close look at below function.
uint16_t rte_vhost_dequeue_burst(int vid, uint16_t queue_id,
struct rte_mempool *mbuf_pool, struct rte_mbuf **pkts, uint16_t count);
This function gets guest buffers from the virtio device TX virtqueue, construct host mbufs, copies guest buffer content to host mbufs and store them in pkts to be processed.
This function supports to use zero copy operation to replace memory copy operation, and it also monitors used mbuf and notify guest that vring is updated.
2.1. Zero Copy
rte_vhost_dequeue_burst() uses copy_desc_to_mbuf() to perform zero copy operation or memory copy operation.
err = copy_desc_to_mbuf(dev, vq, desc, sz, pkts[i], idx,
mbuf_pool);
Virtio front end is using guest phisical address (GPA), and copy_desc_to_mbuf() has to translate this address to host virtual address.
desc_addr = vhost_iova_to_vva(dev,
vq, desc_gaddr,
&desc_chunck_len,
VHOST_ACCESS_RO);
copy_desc_to_mbuf() will check the dequeue_zero_copy flag:
- If dequeue_zero_copy is enabled, host virtual address (HVA) and host phisical address (HPA) would be used as mbuf address, that’s so-called zero copy operation.
- Otherwise, rte_memcpy() is used to copy from host virtual address (HVA) to mbuf.
if (unlikely(dev->dequeue_zero_copy && (hpa = gpa_to_hpa(dev,
desc_gaddr + desc_offset, cpy_len)))) {
cur->data_len = cpy_len;
cur->data_off = 0;
cur->buf_addr = (void *)(uintptr_t)(desc_addr
+ desc_offset);
cur->buf_iova = hpa;
/*
* In zero copy mode, one mbuf can only reference data
* for one or partial of one desc buff.
*/
mbuf_avail = cpy_len;
} else {
if (likely(cpy_len > MAX_BATCH_LEN ||
copy_nb >= vq->size ||
(hdr && cur == m) ||
desc->len != desc_chunck_len)) {
rte_memcpy(rte_pktmbuf_mtod_offset(cur, void *,
mbuf_offset),
(void *)((uintptr_t)(desc_addr +
desc_offset)),
cpy_len);
} else {
batch_copy[copy_nb].dst =
rte_pktmbuf_mtod_offset(cur, void *,
mbuf_offset);
batch_copy[copy_nb].src =
(void *)((uintptr_t)(desc_addr +
desc_offset));
batch_copy[copy_nb].len = cpy_len;
copy_nb++;
}
}
2.2. Monitoring Mbuf
At first, use a linked list to store used mbuf, and update refcnt to avoid wrongly releasing mbuf. And then, send mbuf to other interface.
if (unlikely(dev->dequeue_zero_copy)) {
struct zcopy_mbuf *zmbuf;
zmbuf = get_zmbuf(vq);
if (!zmbuf) {
rte_pktmbuf_free(pkts[i]);
free_ind_table(idesc);
break;
}
zmbuf->mbuf = pkts[i];
zmbuf->desc_idx = desc_indexes[i];
/*
* Pin lock the mbuf; we will check later to see
* whether the mbuf is freed (when we are the last
* user) or not. If that's the case, we then could
* update the used ring safely.
*/
rte_mbuf_refcnt_update(pkts[i], 1);
vq->nr_zmbuf += 1;
TAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(&vq->zmbuf_list, zmbuf, next);
}
After that, iterate this linked list, refcnt 1 means this mbuf is consumed, and this function will release mbuf, update vring and notify guest.
if (unlikely(dev->dequeue_zero_copy)) {
struct zcopy_mbuf *zmbuf, *next;
int nr_updated = 0;
for (zmbuf = TAILQ_FIRST(&vq->zmbuf_list);
zmbuf != NULL; zmbuf = next) {
next = TAILQ_NEXT(zmbuf, next);
if (mbuf_is_consumed(zmbuf->mbuf)) {
used_idx = vq->last_used_idx++ & (vq->size - 1);
update_used_ring(dev, vq, used_idx,
zmbuf->desc_idx);
nr_updated += 1;
TAILQ_REMOVE(&vq->zmbuf_list, zmbuf, next);
restore_mbuf(zmbuf->mbuf);
rte_pktmbuf_free(zmbuf->mbuf);
put_zmbuf(zmbuf);
vq->nr_zmbuf -= 1;
}
}
update_used_idx(dev, vq, nr_updated);
}
2.3. Summary
Vhost-user dequeue zero copy implementation uses shared memory as mbuf address, and DPDK application sends this mbuf to other interface. rte_vhost_dequeue_burst() has to wait for other PMD TX function to free mbuf, and then it can update vring and notify guest. Therefore, other PMD TX function needs to free mbuf timely, otherwise, guest Tx used vring may be starved.
3. Limitations and Issues
3.1. Small Packets
DPDK programmer’s guide suggests that zero copy is not good for small packets (typically for packet size below 512).
Section 2.2 has introduced how to monitor used mbuf in previous section, this overhead is considerable for small packet, and in this case memory copy operation is faster then zero copy operation.
3.2. VM2NIC
DPDK programmer’s guide suggests that guest Tx used vring may be starved if the PMD driver consume the mbuf but not release them timely.
There are three possible configurations to avoid vring starving:
- The nb_tx_desc has to be small enough: <= 64 if virtio indirect feature is not enabled and <= 128 if it is enabled.
- Use smaller tx_free_threshold.
- Increase the size of guest Tx used vring.
PMD TX API needs to release mbuf timely, so that guest TX used vring will not be starved, but performance will be poor. Therefore we need adjust these configurations and find a balance.
3.3. Deep Copy Issue
I uses DPDK 17.11 to test VM2NIC case, and the traffic breaks immediately. After debug I find vq->zmbuf_list is corrupted, and it’s impossible to insert any element.
Please read below code (At lib/librte_vhost/vhost_user.c) for the root cause, it just copy old_vq to vq.
if (oldnode != newnode) {
RTE_LOG(INFO, VHOST_CONFIG,
"reallocate vq from %d to %d node\n", oldnode, newnode);
vq = rte_malloc_socket(NULL, sizeof(*vq), 0, newnode);
if (!vq)
return dev;
memcpy(vq, old_vq, sizeof(*vq));
rte_free(old_vq);
}
For vq->zmbuf_list, tqh_last should point to the first element. But tqh_last is using wrong address after above memory copy operation.
#define TAILQ_FIRST(head) ((head)->tqh_first)
#define TAILQ_INIT(head) do { \
TAILQ_FIRST((head)) = NULL; \
(head)->tqh_last = &TAILQ_FIRST((head)); \
QMD_TRACE_HEAD(head); \
} while (0)
This issue is fixed in DPDK 18.02 release.
When vhost reallocate dev and vq for NUMA enabled case, it doesn't perform deep copy, which lead to
1) zmbuf list not valid
2) remote memory access.
This patch is to re-initlize the zmbuf list and also do the deep copy.